Most notably, economic and trade linkages between with the northern neighbour has maintained strong development, achieving stable and sustainable growth.
On the occasion of the 2025 New Year and the 75th anniversary of both nations’ diplomatic relations (January 18, 1950 - January 18, 2025), Nong Duc Lai, trade counselor of the Vietnamese Embassy in China, discussed with the press the remarkable results achieved in trade exchanges between Vietnam and China last year, as well as the prospects for bilateral trade in the year ahead.
According to Lai, economic and trade co-operation remained a bright spot in bilateral relations in 2024. Amidst a decline in trade between China and many partners, especially major ones, Vietnam stood out as one of the few to maintain stable trade with China, recording double-digit growth in the process. Indeed, Vietnam made up China's fourth-largest trade partner globally and was the largest trade partner from ASEAN.
Bilateral trade continued to grow steadily, with Chinese Customs data indicating that total import-export turnover over the past 11 months of 2024 reached US$235.4 billion, a 14% increase on-year. Two-way trade exceeded the estimated US$250 billion mark by the end of 2024, whilst the export of agricultural products to China continued to maintain strong growth.
The opening of markets for agricultural products has also yielded positive results. The two countries signed a protocol allowing the official export of fresh coconuts, frozen durians, and farmed crocodiles from the country to the Chinese market, a factor contributing to the growth of agricultural exports to China in 2024 and beyond.
Efforts to facilitate trade continue, making it easier for goods to flow in both directions. Since the start of the year, customs clearance at border gates has generally been smooth and relevant agencies and local administrations at both countries' border gates have actively co-ordinated to resolve arising issues, minimizing congestion at border gates during holiday periods and peak seasons, thereby reducing additional costs for businesses.
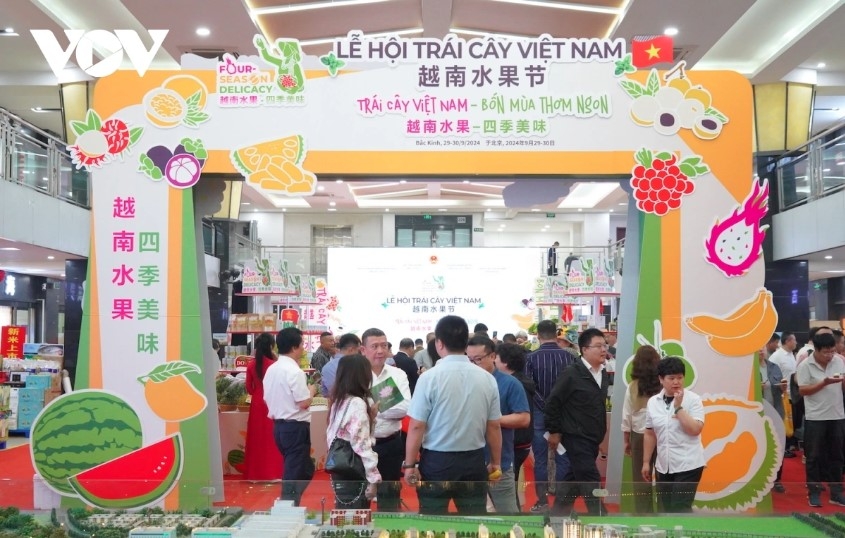
Improved trade promotion activities have supported businesses in connecting with partners, boost market expansion as a contribution to boosting exports, and promoting brand recognition in the Chinese market. Notable examples include the Vietnam Fruit Festival in Beijing and the 'Vietnam Pavilion at the 2024 Asian Food and Beverage Fair in Tai'an City of Shandong province, both of which created a strong impact and positive effects to help Vietnamese agricultural products make deeper inroads into the domestic market and northern region of China.
Furthermore, co-operation between localities from both countries, as well as between Vietnamese ministries and Chinese localities, has been held regularly, capitalizing on local potential and advantages. One notable example is the Memorandum of Understanding on enhancing economic and trade ties between the Ministry of Industry and Trade of Vietnam and the People's Administration of Shandong province, which has laid the foundation for stronger collaboration with a key economic region in northern China.
Looking ahead to trade prospects in 2025, Lai stated that with the current positive development of bilateral relations, high-level visits over recent years has provided additional momentum for co-operation and laid the foundation for sectors, localities, and businesses to deepen and expand ties across all fields, with economic and trade relations continuing to serve as a vital pillar.
During these visits and discussions between high-ranking leaders of both countries, numerous agreements were signed, the majority of which pertained to economic and trade collaboration. These agreements will serve to create a solid basis for trade relations between the two nations in 2025 and the years ahead. In addition, Vietnam will continue to leverage its geographic advantage as a neighbour to China, taking full advantage of opportunities within the Vietnam-China co-operation framework, such as the China-ASEAN Free Trade Area (CAFTA), the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), and bilateral and multilateral co-operation mechanisms to tap into the potential of the 1.4 billion-strong Chinese market.